Autonomous electronic stimulator
of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes
"ELECTRONIC NORMALIZER"
Clinical Efficiency And Mechanisms Of Effect

Autonomous electronic stimulator
of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes
"ELECTRONIC NORMALIZER"
Clinical Efficiency And Mechanisms Of Effect
The material represented in this review concerns only the EN
articles (design MACÈ 943115.002, Technical Instruction TY 9444-014-11555014-95) produced
by the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
The major precondition for the investigations performed was the known physiological fact of local and general response of intestinal musculature to electrostimulation of the sections thereof (18). Moreover, the secondary effect was discovered, namely, activation of intestinal motor system up to several days after termination of electrostimulation.
In Russia, electrostimulation of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) was widely developed since late 1960s. The researchers selected the electric current parameters capable to activate the intestinal functions rather effectively (they demonstrated the advantage of alternating electric signal in relation to direct current and bipolar electrostimulation in relation to monopolar electrostimulation), and designed instruments for transgastral (4), transduodenal (5) ), and transrectal (8) electrostimulation. The information was obtained on positive clinical effect to postoperative intestinal pareses, disorders of GIT motor system for patients with spinal trauma (6), generalized peritonitis (12), chronic pancreatitis (2, 8), and diskinesia of billary ducts (8).
In addition to intra-abdominal electrostimulation using probes connected with devices generating electric current, the techniques of intratissue electrostimulation were developed that involved implantation of electrodes to walls of stomach, duodenum, and small intestine,(3, 20), as well as transcutaneous electrostimulation of abdomen(4, 10, 19).
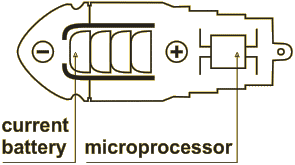
In 1980s, the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract (AES GIT) was developed for application in surgery, that, unlike earlier instruments for GIT electrostimulation, was designed as a swallowed capsule (9). The walls of this capsule are electrodes; the power source and the generator of electric signal are inside the capsule.
The advantage of this method of electrostimulation is the possibility to affect consequently all the alimentary tract. Meanwhile, the direct contact with the GIT walls enables to reduce significantly the current to produce the adequate effect and, therefore, to avoid unpleasant subjective perceptions and side effects during the procedure.
This technique gave rise to additional requirements to materials of the case of the electrostimulator. It was necessary to achieve biological indifference (if no electrophoresis of elements was prescribed), maximum stability to changeable properties of active media, ability to maintain invariable the electric signal parameters given. In the study of electrode characteristics in various media (hydrochloric acid, bile, etc.), it was discovered that steel 12Cr18Ni9 is the most acceptable material among such materials as titanium, carbon graphite, steel, carbon glass (21).
The electric signal fed to the electrodes of AES GIT simulated the electric intestinal activity. When AES GIT passed the alimentary tract, packages (with the average duration of 0.5 seconds) of rectangular pulses with the length of 3 to 5 seconds and the frequency of 35 to 50 Hz are generated every 2.5 to 3.5 seconds (9).
A series of experimental investigations was performed with normal dogs and those with reflective GIT paresis. The strengthening effect was observed in the motor system of GIT, while local and general motor reaction was observed with the aftereffect under normal conditions.
Under clinical conditions, AES GIT was applied for treatment of postoperative pareses of 39 patients, who were urgently hospitalized. The positive effect was observed for 82% of patients in the form of strengthening of the motor function of GIT during the first three days after use. In addition, 30 patients with planned operations were studied; AES GIT was prescribed for preventive purpose. The positive effect was recorded in 73% of cases. Combined application of AES GIT and prolonged mesenteric Novocaine blockade enabled to achieve prevention of heavy forms of postoperative GIT paresis.
Thus, this review shows that GIT electrostimulation is rather widely used in advanced medicine, and the instruments are permanently improved. In our opinion, however, the fields of application of this method were narrowed and virtually restricted to diseases of GIT, pancreas, and billary ducts.
Further investigations performed by the ECOMED Research and Production Association determined the guidelines of autonomous electrostimulation and field effect on the human organism. The investigations demonstrated the dependence of the efficiency of influence on the slope of pulse fronts, deviations of the on-off time ratio, modulation of the signal envelope, and carrying frequencies in the spectrum of electromagnetic field irradiated.
Nowadays, ECOMED Research and Production Association produces and develops advanced models of autonomous electronic stimulators, normalizers, and optimizers) (Patent "Electronic stimulator" ¹ 1632 dated 28.12.93), which are significantly different from AES GIT in their design, output signal parameters, and efficiency, in particular, EN (Patent "Electronic normalizer" ¹ 2071368 dated 0.01.96, International Patent "Electronic normalizer" PCT/RU/00023 dated 31.01.96).
The first AES GIT&MM - EN instruments appeared in 1991. Comprehensive initial investigations were carried out in the Tomsk Medical Institute by ECOMED researcher, Professor V.V.Pekarskii, a Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. EN can produce a positive effect on patients with gastritis or gastral or duodenal ulcers; treatment is accompanied with positive changes in the composition of parietal mucus, gastric juice, and acidity (Protocol of medical examinations of serial AES GIT&MM specimens dated December 30, 1992, Siberian Medical University, signed by Rector M.A.Medvedev, Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences). Unlike AES GIT approved by the Ministry of Health Protection for GIT applications, EN can be applied also in other internal systems of the organism (vagina, uterus, and duct systems) as well as with galvanic coatings for uniform introduction of deficient microelements, according to the conclusion on toxicological examinations in the All-Russia Research Institute of Medical Technology dated June 8, 1995 and signed by Director B.I.Leonov
Further experimental and clinical investigations are
carried out to reveal the correlations and mechanisms of effect of electric and field
influence through GIT and adjacent organs on the whole organism; the list of indications
for use is extended. Some results of these investigations are represented below.
Launching the process of urgent adaptation, the stress reaction
simultaneously produces the injuring effect that can negatively affect the functioning of organs
and systems, in particular, the adaptation system (7, 11).
With the decreasing negative stress effects and strengthening
adaptation response, functioning of the whole organism changes including the mechanisms of
protection and adaptation to injuring factors at the level of systems, organs, and tissues.
As a result, the survival and efficiency of human functioning under overloading increases,
the status in acute and subacute periods of urgent pathology (trauma, burns, myocardial
infarct, etc.) is improved, the periods of recovery are shortened, and the life quality
after the disease is improved.
The systematic activation of adaptation system may result
in transition to a higher level of functioning of the mechanisms of antistress and adaptation
readiness of the organism without any harm thereto. At the same time, the skills of physical
and mental training are improved, the energy expenses of the organism are reduced together
with the side reactions of the training process, which is necessary to achieve the final
result. Moreover, in addition to the positive effect in acute pathology, it becomes possible
to prevent really exacerbations and completely treat heavy chronic diseases of various origin.
In this connection, it is clear that the facilities, which
can really and quickly neutralize the negative effect of stress reaction and activate the
adaptation processes, are of great interest. They should primarily include the methods, which
directly or indirectly normalize the functions of neuroendocrine centers. A special interest
is represented by medicament-free methods without contraindications or side effects
The quality of formation of urgent and long-term adaptation
essentially depend on the functioning of neuroendocrine systems. One of the major systems
is the opioid system of brain generating above 40 neurohormones (opioid peptides). The major
purpose of this system is protection from stress injuries, anesthesia and balance of functioning
of the organs and tissues of the whole organism. The second system, which determines the
adaptation response, includes hypothalamus and hypophysis. Its major function is adjustment
of activity of endocrine glands and all the kinds of tissue metabolism to different
conditions of external and internal media (7, 11).
The status of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) takes an essential
part in formation of the adaptation response. On the one hand, its functioning is directly
associated with generation of a series of hormones,which display not only local but also the
general activity (in particular hormones of pancreas, opioid system of GIT, etc.); and, on
the other hand, disorders in the GIT activity produce a negative effect on the status of
the immune system, all kinds of metabolism at the tissue level, etc.
One of the known methods to correct the adaptation system involves
he Autonomous Electronic Stimulator of GIT and Mucous membranes or the Electronic Normalizer (EN),
which produces the direct effect on GIT and indirectly affects the adjacent systems of the organism, in
particular, the neuroendocrine system. The feature of the EN effect is stable increase of the level of
adaptation readiness of the organism after every administration of EN. This accumulation results in a
relatively fast adjustment of the organism to the regime of operative (if necessary) switching reserves
and resources, which are not required or used either in standard life or under the effect of pathogenic factors.
The investigations performed by the ECOMED Research and
Production Association enable to state both the direct tactical effect of EN, for example, for the purpose
of detoxication, and the indirect strategic effect of EN on systems of organs through the peripheral nervous
system on opioid system, hypothalamus and hypophysis, then on neurohormones, with further
correction of the status of systems and organs with the change in all the kinds of balance
and metabolism. This complex effect finally increases the adaptation readiness and resistance
of the organism to external overloading factors and diseases of internal organs.
The improvement of functions of various GIT sections and the
adjacent organs, normalization of functioning of endocrine glands and, apparently, exhaust of
biologically active GIT peptides to circulating blood, and change in afferent impulsation in vegetative
nervous system normalize functioning of neuroendocrine systems of brain and, therefore, change the status
of the adaptation system, normalize the activity of immune and other systems of the organism.
Thus, the electromagnetic field arising as a result of interference of
the filed generated by EN and the own electromagnetic field of the organism can change the status of
control systems. Therefore, EN is the method to correct the adaptation system of the organism
and can produce the therapeutic effect not only in GIT pathology, but also in the diseases of other
organs and their systems.
In the cases aforementioned, the following effects are observed:
In the experimental part of work, acute obturation obstruction
of small intestine was simulated with ten dogs (Moscow). After a single EN administration,
bioelectrical and motor intestinal functions were normalized, circulation and metabolism of
intestinal wall were improved. Thus, the contraction activity increased more than 2.4-fold,
the amplitude of fast and slow components of biopotentials significantly increased, and
adhesion potentials appeared. The pulse curve amplitude in the rheogram increased 1.7-fold,
and the intestinal wall oxygen tension increased 2.3-fold.
In a day after administration of EN, the patients with
postoperative pareses showed positive dynamics: abdominal swelling reduced together with pain,
peristaltic noises appeared, gases began to release, and nine of fifteen patients had normal
stool. The electric activity parameters improved. In two days, the phenomena of intestinal
pareses were settled for all the patients; the intoxication leukocyte index changed to
normal values. In the control group of 9 patients, normalization of parameters was observed
only in seven days after the operation.
After administration of EN, the patients with gastritis (11 patients)
showed the increase in the absolute protein amount in both the parietal mucus and in the molecule of
mucus (reduced degree of glycosilation). Certain increase was observed in the concentration of proteins
and sialic acid in the nonstructural fraction of mucus as well as in the concentration of fucose, galactose,
and nucleic acids in the gastric juice.
At the background of EN administration, the patients with
gastroduodenal syndrome showed reduced acidity of gastric juice and the concentration of galactose and
fucose in the nonstructural fraction of mucus.
In the case of noncalculous cholecystitis and diskinesia of billary
ducts (11 patients), the ultrasound examination revealed the favorable EN effect on the motor and
evacuator functions of the gallbladder (15 to 20% increase in the contractibility) and on the billation
function of smaller (intraliver) ducts.
Investigations of the EN effect on the functional status of large
intestines of the patients with chronic large intestinal stasis (CLIS) and large intestinal irritation syndrome
(LIIS) were carried out in the Laboratory of Clinical Pathophysiology with the Group of Physical
Therapy, State Research Center of Proctology, Russian Federation Ministry of Health Protection
and Medical Industry (Moscow). The report dated July 28, 1995 was signed by Professor
G.I.Vorobiov, Director of the State Research Center of Proctology, Corresponding Member
of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences; the program of investigations was approved by
the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
These investigations involved 23 patients (eight men and fifteen
women aged 38 to 57): seven patients with CLIS and sixteen patients with LIIS. During the observation,
EN was twice administered by seventeen patients (the second administration was performed in a day after
removal of the first EN) and six patients had single administration of EN.
Removal of EN with normal stool was observed in the first two
days after administration for 50% of patients and on the seventh day for the female patient with
decompression form of CLIS (after administration of purgative); the rest patients removed
EN with normal stool in three to five days after administration.
During eight-week observation, 75% of patients had normal stool,
while five patients with CLIS still showed constipations.
The motor and evacuator functions of large intestines were
determined by means of multichannel stimulation balloonography.
Initially, all the patients showed a significant reduction
in the electrical activity of large intestines (Figs. 1 and 2) expressed in the increased
index of activity, amplitude, and duration of motor activity waves.
Recent concepts on the mechanisms of EN effect
As is known, the status of human organism under overloading
(mental and physical, toxic and ecological effects, acute diseases or heavy exacerbation of
chronic processes) depends on the status of adaptation system and the quality of adaptation
response.
Electronic Normalizer (EN) has the following effects:
Indications to application:
Medical:
Sports, dispatching services, working activity under increased physical or mental loading and
under extreme conditions.
Application of EN is also recommended for persons with the lack of motion (sedentary work).
Contraindications:
mechanical intestinal obstruction and cicatrical stenoses.
Efficiency of EN in diseases of gastrointestinal tract
Investigations of the EN effects on the motor and evacuator
functions of intestines and gallbladder as well as on the composition of mucus and parietal
digestion for patients with postoperative intestinal paresis, chronic noncalculous cholecystitis,
gastritis, ulcer of stomach or duodenum were carried out in the Chair of Experimental and
Clinical Surgery, Russian State Medical University (Moscow). The report dated June 24, 1995
was signed by Professor G.I.Storozhakov, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Vice-Rector of the Russian
State Medical University and by Professor B.K.Shurkalin, Head of the Chair; the program of
investigations was approved by the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
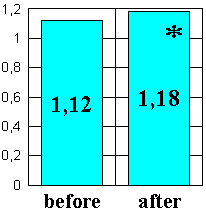
Figure 1. | Dynamics of the activity
index of large intestine in the case of pathology on the background of EN administration. |
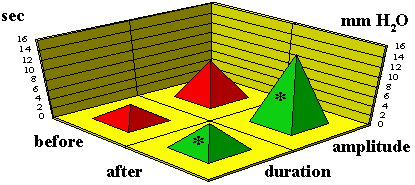
Figure 2. | Parameters of GIT motor
activity waves for patients with pathology of large intestines upon EN administration. |
Thus, administration of EN for regeneration of the motor and electrical activities of large intestines has pathogenetic grounds. At the same time, the muscular activity of large intestine is effectively regenerated, apparently, due to the influence on nervous and muscular endings and regeneration of the receptor apparatus. For most patients, the general status was improved together with improvement of neuropsychological status, decreased weakness and fatigue, normalization of sleep. The reduced asthenoneurotic syndrome was accounted for by the reduced symptomatics of the basic disease, on the one hand, as well as by the indirect influence on the neuroendocrinic centers, on the other hand.
Conclusions:
For the purpose of investigation of the EN effect on the
status of patients and the lipid metabolism in diabetes and primary hyperlipidemia,
clinical investigations were carried out in the First and Second Endocrinological Divisions
of Hospital No. 67 (Moscow), which is the basis division of the Chair of Endocrinology, Faculty
of Advanced Medical Studies, Moscow Medical Academy named after I.M.Sechenov and the Institute
of Diabetes, All-Russian Endocrinological Center, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. The report
dated March 18, 1992, the act dated December 24, 1992, and the conclusion No. 10/03/-046B dated
January 27, 1995 were signed by Professor M.I.Balabolkin, Director of the Institute of Diabetes,
All-Russian Endocrinological Center, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences; the program of
investigations was approved by the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
The observation involved 28 patients including 22 patients with diabetes
and six patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
Table 1 represents the distribution of the patients in relation
to the type of diabetes, sex, and age.
Table ¹ 1
Application of EN for diabetes
(Patent "Method of change of lipid metabolism" N 2071379 dated 29.01.96).
| Disease | M | F | Age | ||||
| 34 - 45 | 46 - 55 | 56 - 65 | over 66 | ||||
| Diabetes type I | 7 | 3 | 6 | 4 | --- | --- | 25 - 36 |
| Diabetes type II | 4 | 8 | --- | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 2 | 4 | --- | --- | 2 | 4 | --- |
As is seen from Table 1, all the patients with diabetes type I were 25 to 45 years old, while all the patients with diabetes type II and hyperlipidemia were over 45. The duration of diabetes ranged 4 to 20 years. Fourteen patients (ten with diabetes type I and four with diabetes type II) received insulin therapy. Eight patients with diabetes type II received peroral sugar-reducing preparations (Maninyl, Oramide, or Adebite with the daily dosage of 2 or 3 tablets).
Table 2 represents the parameters of carbohydrate metabolism for the patients with diabetes in relation to the degree of compensation.
Table ¹ 2
| Glycemia, mmol/l | Glycosuria, g | ||
| on an empty stomach | at noon | ||
| 1. Patients with diabetes type I: | |||
| a) status of compensation | 6,20 ± 1,10 | 8,92 ± 1,05 | 5,00 + 0,43 |
| b) status of subcompensation | 7,32 ± 0,92 | 11,60 ± 2,11 | 24,30 ± 5,20 |
| 1. Patients with diabetes type II: | |||
| a) status of compensation | 5,80 ± 1,08 | 8,66 ± 0,94 | |
| b) status of subcompensation | 7,41 ± 1,12 | 12,40 ± 3,60 | |
Eight patients with diabetes type II and five patients with hyperlipidemia showed extra weight, which exceeded the ideal weight by 34 ± 4.9%. The patients with hyperlipidemia received no medicamental therapy.
Seven patients under observation had double administration of EN. The second administration was performed in 30 days after clinical and laboratory investigations. In 30 days after the second administration of EN, the clinical and laboratory investigations were repeated.
During all the period of observation, no patient with diabetes showed decompensation of the basic disease.
In order to study the status of lipid metabolism, cholesterol, low-density lipoproteides (LDLP), high-density lipoproteides (HDLP), and triglycerides were determined for all the patients.
The study of the basal level of cholesterol and triglycerides for the patients with diabetes type I indicates their high values (6.55 ± 1.20 mmol/l and 2.05 ± 0.01 mmol/l. respectively). For healthy persons, the plasma levels of cholesterol and triglycerides ranged from 3.9 to 6.5 mmol/l and up to 1.9 mmol/l, respectively.
Figure 3 represents the parameters of lipid metabolism for the patients with diabetes type I before and after double administration of EN. As is seen, already after the first administration of EN, certain reduction of triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDLP takes place simultaneously with a significant increase in HDLP. In 30 days after the second administration of EN, we observe further reduction in triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDLP to subnormal values and a significant increase in HDLP that indicates the exclusive efficiency of EN. The clinical observation included stable compensation of diabetes for the patients. Already in a week after the first administration of EN, six of ten patients showed a reduction in their need in insulin, and the average dosage was decreased by 5 to 10 units.
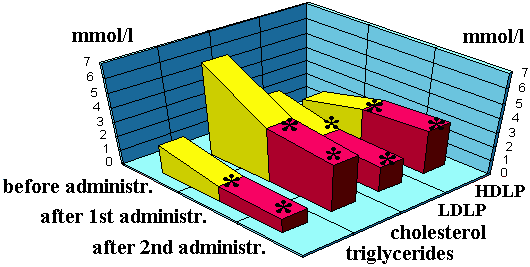
Figure 3. | Dynamics of the
lipid metabolism parameters for the patients with diabetes type I upon administration of EN (p < 0.05 in relation to the initial value). |
Figure 4 represents the results of investigation of the patients with diabetes type II before and after double administration of EN. As is seen, the patients with diabetes type II also show hyperlipidemia as those of type II. On the background of EN administration, we observe reduction in cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDLP and increase in HDLP. In comparison of the analogous parameters of the patients with diabetes type I and II, no significant difference was observed.
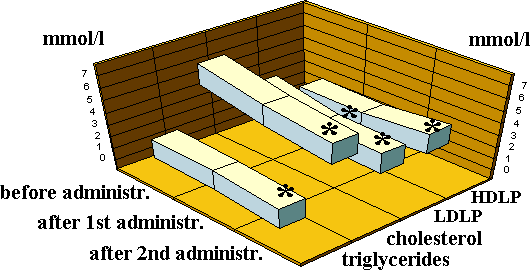
Figure 4. | Dynamics of the lipid
metabolism parameters for the patients with diabetes type II
upon administration of EN (p < 0.05 in relation to the initial value). |
Table 3 represents the results of lipid investigations for the patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
Table ¹ 3
| Time of EN administration | n | Triglycerides, mmol/l | Gholesterol, mmol/l | LDLP, mmol/l | HDLP, mmol/l |
| Before | 6 | 2,70 ± 0,25 | 10,57 ± 1,70 | 8,50 ± 1,06 | 0,97 ± 0,02 |
| 30th day after 1st administration | 6 | 2,10 ± 0,04 | 9,80 ± 1,20 | 8,30 ± 1,20 | 1,05 ± 0,02 |
| 30th day after 2nd administration | 6 | 1,90 ± 0,06 | 6,10 ± 1,46 | 7,80 ± 0,40 | 2,40 ± 0,24 |
As is seen from Table No. 3, the average values of triglycerides, cholesterol, and LDLP significantly exceed the upper limits of the normal parameters. On the background of EN administration, all the patients with primary hyperlipidemia show an increase in HDLP and a reduction in the rest parameters. In 30 days after the first EN administration, these patients show a stable improvement in the ECG parameters.
The results of investigations performed by many scientists both in Russia and abroad indicate the presence of hyperlipidemia in 40 to 60% of adult population. There are various reasons for development of hyperlipidemia. They include the alimentary factor, metabolic disorders, genetic factors, etc. The lipid metabolism depends upon the enzyme systems, in particular, lipoproteinlipase (LPL). In the case of insulin deficiency or insulin resistance, the LPL synthesis decreases that is one of the major reasons for hyperlipidemia in diabetes.
Cholesterol, triglycerides, and phospholipides are transported in the form of lipoproteides. Lipids are insoluble in water; therefore, the evolution resulted in the complex system of their transport and distribution in such medium as blood. The composition of LDLP includes 60 to 70% of all the plasma cholesterol.
For an adult person, liver and peripheral cells and tissues remove from blood almost 2/3 of lasma LDLP. Due to the HDLP capacity to collect cholesterol, esterify it and convert into the forms, which undergo further transformations in liver, they are considered as lipoproteides preventing development of hypercholesterolemia.
Thus, the study of lipid metabolism status in the group of patients under investigation indicates the presence of changes, which are characteristic for atherosclerosis. This fact produces the risk of vascular diseases, especially, because there is a simultaneous increase in LDLP and reduction in HDLP.
Until recently, there is no universal preparation for treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia. The results of EN effect enables us to hope in its wide application and high efficiency. Most likely, the mechanism of EN effect involves stimulation of LDLP capture and excretion of cholesterol by liver. In addition, liver electrostimulation may result in stimulation of LPL activity. In turn, LPL promotes hydrolysis of triglycerides yielding free fatty acids (FFA), which enter the cells and undergo oxidation. Finally, EN passes all the sections of alimentary tract and stimulates formation of HDLP, which promote the back transport of cholesterol from tissues to kidneys and its excretion with billary acids.
Application of EN caused no negative side effects for any patient. No negative changes were observed in relation to parameters of clinical blood or urine examinations. All the patients were subjected to eye fundus examination and ltrasound study of pancreas.
Nobody showed any negative dynamics.
We observed stable recovery of morning erection and growth in sexual potency for men, especially for those with excessive weight.
Conclusions:
Figure 5. |
Bronchial conductivity on the background of EN therapy (%). |
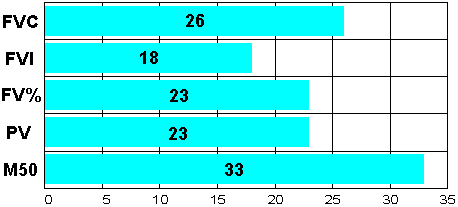
Figure 6. |
Parameters of the external breathing function on the background of EN therapy (% of increased parameter). |
After EN application, we observed a certain reduction of the blood concentration of immunoglobulin E (more than 2-4-fold for 30% of patients) and an increase in the concentration of immunoglobulin A (Fig. 7).
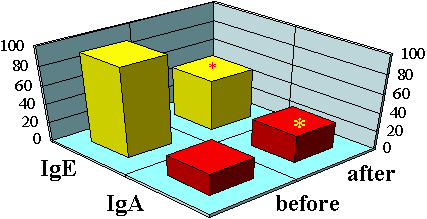
Figure 7. | Dynamics of immunological parameters on the background of EN therapy for patients with bronchial asthma. |
This fact indicates the decreased intensity of allergic inflammation and stimulation of immunological protective mechanisms. In bronchial asthma, the synthesis of IgE antibodies is realized first in mucosa of respiratory ways and in regional lymph nodes, where the precursors of IgE synthesizing B-cells undergo the stages of differentiation, acquire IgE receptors in addition to IgM receptors, which are present in all the types of lymphocytes. The reduced level of Ig production of E-antibodies indicates suppression of the immune response. A possible mechanism of this effect is the influence on the B-cells of intestinal lymph nodes by the electromagnetic field of low frequency generated by EN (1, 13, 14, 15, 16).
Eosinophilia with bronchial asthma is considered as an indicator of the reversible component of bronchial obstruction. Eosinophiles, which form cellular infiltration of the mucosa of respiratory ways, are the major source of mediators, which cause bronchismus and edema of bronchial mucosa, stimulate mucus secretion, injure bronchial epithelium, and release toxic peroxide metabolites. Each eosinophile circulating with blood corresponding to 500 eosinphiles in tissues.
Therefore, the eosinophile reduction in blood, observed upon EN administration (Fig. 8), indicates the EN effect in essential pathogenetic mechanisms of bronchial asthma.
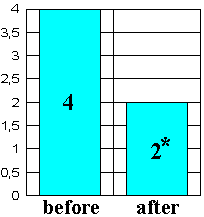
Figure 8. |
Blood concentration of eosinophiles on the background of EN therapy for patients with bronchial asthma. |
Conclusions: The investigations of the EN efficiency for twenty
patients (ten men and ten women) with prolonged (one to three months) exacerbation of
lumbosacral radiculitis were carried out in the Chair of Neurology and Neurosurgery,
Russian State Medical University (Moscow). The report dated September 12, 1995 was
signed by E.I.Gusev, Head of the Chair, Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences,
Chairman of the Section of Neurology, Scientific Council of the Russian Federation
Ministry of Health Protection; the program of investigations was approved by the ECOMED Research
and Production Association on December 21, 1994.
Ten patients (five men and five women comprised the major group
(EN therapy), and the rest ten patients comprised the control group, who administered a placebo.
After EN administration, the control group showed the tendency
to the significant progress of neurological processes, especially, to the decreased expression of
pain syndrome, to the progress of tension symptoms and fall of sensitivity.
During the treatment, no patient of the control group showed
recovery of radicular disorders of sensitivity (Fig. 9).
Effect of EN on the status of patients with lumbosacral radiculitis
(Patent "Method of Influencing Psychiatric and Psychoneurological Peculiarities
of the Body" ¹ 96111949 dated 26.06.96)
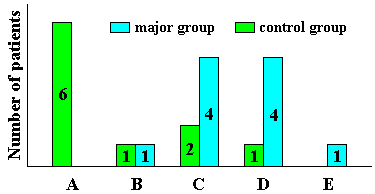
Figure 9. | Distribution of the
patients with lumbosacral radiculitis in relation to the therapeutic effect.
A - complete regress of symptoms; B - significant; C - moderate; D - no significant dynamics; E - worse status. |
In the point estimation of neurological symptoms, the major group showed a certain regress of neurological deficiency, whereas the positive dynamics was statistically uncertain in the group of patients, who administered a placebo.
An interesting feature of the EN effect was the recovery of vegetative reactions lost by the patients with lumbosacral radiculitis, namely, appearance of skin dermatitis below girdle and in the region of lower limbs. In two to four weeks, white dermoraphism changed into normal pink that indicated the recovery of normal vegetative skin reflexes, which were not observed for the patients, who administered a placebo.
According to the data of electromyography, the major group (unlike the control group) showed:
The expressed clinical effect of EN on the background of degenerative changes caused by the chronic spinal disease confirms the vegetative and trophic effects. A fast disappearance of stable neurological symptoms indicates the neuroreflex influence. The adaptive and trophic effects of EN observed on the background of activation of sympathetic system appears in the form of normal vegetative patients reactions below girdle. Meanwhile, we observe a stable normalization of the functional status of the vegetative nervous system.
Conclusions: The investigations of the EN effect on the affective and emotional
spheres and sexual function of the patients with sexual and affective disorders on the background of
somatic aggravation (excess nutrition and disorders of metabolism) were carried out in the Moscow
Research Institute of Psychiatry. The report dated March 15, 1995 was signed by Professor
V.N.Krasnov, Director of the , Research Institute of Psychiatry, Russian Federation Ministry of Health Protection;
the program of investigations was approved by the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
The major group included twenty men, who administered
EN twice with the interval of two weeks. The patients in the control group (nineteen men)
administered a placebo. The age of patients ranged from 32 to 48 years old. The duration of sexual
disorders ranged from two to seven years. In their clinical diagnosis, they related to the group of
secondary sexual disorders on the background of endocrine and somatic (including inflammatory
urological) diseases. In their initial status, distribution of complaints, and other parameters, both
groups of patients were comparable.
The following dynamics of complaints was observed on the
background of EN application (Fig. 10):
Application of EN in psychiatry
(Patent "Method of Influencing Psychiatric and Psychoneurological Peculiarities of the Body" ¹ 96111949 dated 26.06.96)
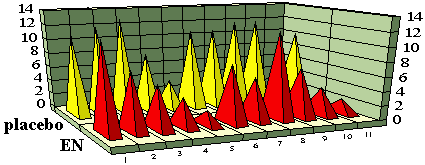
Figure 10. | Number of patients
with sexual disorders and various complaints on the background of EN administration.
Complaints: 1. decrease in working capacity; 2. irritability; 3. headaches; 4. insomnia; 5. somnolence; 6. decreased libido; 7. absence of erection; 8. shortened coitus; 9. nausea; 10. unpleasant feeling in genitals; 11. dryness in oral cavity. |
As is seen from Fig. 10, the patients with sexual and affective disorders upon the EN treatment reduced their complaints for irritability, headaches, disorders of sleep, and sexual disorders. Moreover, as a result of the EN therapy, the sexual initiative increased from 6 to 9 points together with the quality of coitus (from 6 to 10 points).
In the first two days after EN administration, the patients showed normalization of the affect (rise in temper, improvement of sleep, and appearance of activity). The similar effects were retained up to two weeks and fixed after the second EN administration. The testing with Luscher color test fixed an increase in the overall working capacity from 53 to 67% as well as a decreased deviation from the autogenous standard from 43 to 28% that indicates the complex multilevel effect of EN.
Conclusions: In order to verify the possible effect of EN on tumor cells,
the investigations were carried out on direct and indirect tumoricidal activity of EN in short-term
and long-term cellular structures as well as in combination with antitumor medicinal preparations
(Research Institute of Pediatric Hematology, Moscow; the reports dated December 22,
1994 and June 1, 1995 and the conclusion No. 12-95/3 dated March 21, 1995 were signed by
Professor A.G.Rumyantsev, Director of the Research Institute of Pediatric Hematology,
Russian Federation Ministry of Health Protection, Corresponding Member of the Russian
Academy of Medical Sciences; the supervisor of investigations was Professor L.G.Korkina,
Doctor of Medical Sciences; the program of investigations was approved by the ECOMED
Research and Production Association.
The objects under investigation included peritoneal rat
macrophages, ascites lymphoma EL-4E, and sarcoma MCA/77-23 (clone H). The tumors were
inoculated to 8-10 week aged mice of line C57BL (H-2K).
1. The influence on EN on production of oxygen radicals
and the tumor necrosis factor by peritoneal macrophages.
The production of free oxygen radicals by macrophages was
estimated by intensity of luminol-dependent and lucigenin-dependent chemiluminescence (CL)
(spontaneous and activated by latex particles). For investigation of the influence on the oxygen
radicals production, EN was placed into the culture of macrophages and performed sampling of
cells for analysis in 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes. The idle EN was placed into the control culture.
The production of the tumor necrosis factor (alpha-TNF) by
peritoneal macrophages was determined by the immunoenzyme method. EN was placed into the
ñulture of macrophages for 1, 2, and 2.5 hours, and the alpha-TNF production was measured in 24
hours of incubation of cells under sterile conditions.
It was observed that EN makes a statistically significant strengthening
of the spontaneous luminol-dependent CL and suppresses the spontaneous lucigenin-dependent CL (Table A).
Table A
Antitumor properties of EN
(Patent "Method of Increase of the Body Resistence to tumors" ¹ 2071367 dated 31.01.96).
| Incubation time, min | Intensity of luminol CL, (% of control) | Intensity of lucigenin CL, (% of control) | ||
| 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 30 | 152 | 161 | - | - |
| 60 | 280 | 0 | 23 | 75 |
| 120 | 196 | 0 | 23 | 75 |
| 180 | 148 | 0 | - | - |
Simultaneously, we observe the suppression of luminol- and lucigenin-dependent luminescence activated by latex particles. The maximum activating effect of EN was recorded in 60 minutes of joint incubation (strengthening effect of 280%). Strengthening of the luminol-dependent CL indicates the increased production of oxygen radicals generated upon decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. As was demonstrated in some investigations, just these radicals have the greatest cytotoxicity with respect to tumor cells. On the contrary, the lucigenin-dependent CL registers generation of physiologically essential superoxide radicals, which, however, do not virtually affect the vitality of tumor cells.
It is noteworthy that the maximum strengthening in production of the tumor necrosis factor by phagocyte cells (Table B).
Table B
| Time of incubation with EN, min | Concentration of alpha-TNF, pg/ml |
| 0 30 60 120 180 |
117 ± 43 151 ± 24 237 ± 68 164 ± 35 102 ± 38 |
Thus, EN increases the antitumor activity of phagocyte cells and intensifies generation of oxygen free radicals registered by means of luminol-dependent CL, and increases the production of the tumor necrosis factor by the cells.
2. The Influence of EN and chemical preparations on vitality of cells in the culture.
The vitality of cells in the culture was estimated by means of a vital dye, trypan blue. The percentage of uncolored (vital) cells in the culture was calculated.
As medicinal preparations, metatrexate (Ebewe Anzneittel, Austria) and vinchristine (Gedeon Richter, Hungary) were used. The chemical preparation of metatrexate was used in the amount of one therapeutical dose (TD) of 3 mg/l, 0.5 TD, and 0.1 TD; the plant preparation of vinchristine was also used in the amount of 1 TD (0.1 mg/l), 0.5 TD, and 0.1 TD.
The average number of vital cells in the lymphoma culture was 91.9 ± 3.6%. After four hours of incubation, the number of vital cells in the culture was virtually invariable and equaled 89.2 ± 2.1%. In the experimental cultures, the corresponding parameter was as follows:
|
- 88,2 ± 1,9% - 85,6 ± 2,7% - 86,1 ± 2,3% - 83,9 ± 2,0% - 82,9 ± 3,1% |
3. The influence of EN and chemical preparations on the proliferation rate of tumor cells in the cultures.
Cells EL-4 and MCA/77-23 were cultivated in 24-hole board (Costar) in the medium of RPMI-1640 containing 10% of embryonic calf serum, HEPES buffer, L-glutamine, indispensable amino acids, sodium pyruvate, antibiotics, and 2-mercaptoethanol. In various times after the beginning of cultivation, the level of 3H-thymidine was determined; for this purpose, the cells were transferred to 96-hole boards (NUNC) (50000 cells per hole), 3H-thymidine was added, and the cells were cultivated for one hour. Then the cells were transferred to a filter using a harvester, and the level of radioactivity was determined using a beta-counter (Beckman). The intensity of DNA synthesis in the tumor cells was determined by inclusion of 3H-thymidine; for this purpose, 50000 tumor cells were incubated in the presence of tritium-labelled thymidine for one hour, then the cells were transferred to a filter and the level of radioactivity was determined.
The results were expressed as the index of suppression of 3H-thymidine inclusion (I = number of pulses in the experimental culture/number of pulses in the control culture).
Every point was measured in triplicate. Five independent experiments were performed. The statistical treatment was carried out using the Student method assuming 5% as the criterion of reliable difference between the experimental and control results. Table C represents the resulting experimental data.
Table C. Suppression of 3H-thymidine inclusion upon incubation
with EN and chemical preparations.
| Agents | Dosage, time of incubation | Inclusions of labelled thymidine |
| - | - | 1,0 |
| EN | 4 hours | 0,630 ± 0,015 |
| Metatrexate | 1.0 TD, 24 hours | 0,022 ± 0,008 |
| Metatrexate | 0.5 TD, 24 hours | 0,035 ± 0,009 |
| Metatrexate | 0.1 TD, 24 hours | 0,140 ± 0,030 |
| EN + Metatrexate | 0.1 TD, 24 hours | 0,048 ± 0,008 |
| Vinchristine | 1.0 TD, 24 hours | 0,018 ± 0,001 |
| Vinchristine | 0.5 TD, 24 hours | 0,030 ± 0,007* |
| Vinchristine | 0.1 TD, 24 hours | 0,130 ± 0,030 |
| EN + Vinchristine | 0.1 TD, 24 hours | 0,050 ± 0,010* |
As is seen, incubation of the tumor cells with the EN autonomous electrostimulator resulted in suppression of inclusion of the radioactive label into DNA. Virtually the same results were obtained in determination of the suppression index immediately after termination of the action. Therefore, we can conclude that the prolonged inhibiting effect of electromagnetic field is retained in the culture of vital tumor cells at least for one day.
The investigations on the influence of metatrexate and vinchristine on suppression of lymphoma cells proliferation immediately after termination of the action showed absolutely no effect: the cells continued the DNA synthesis at the previous rate. The combined influence of EN and chemical preparations discovered that immediately after termination of incubation all the observed inhibiting effect on proliferation depended on the presence of the stimulator in the medium for cells incubation.
The inhibiting effect of chemical preparations becomes expressed only in 24 hours after incubation. In the experiments, metatrexate and vinchristine completely terminated the DNA synthesis in the tumor cells that indicated 100% death of the lymphoma cells. It is interesting that death of the tumor cells under the influence of chemical preparations was primarily apoptopic rather than necrotic. Under these conditions of virtually complete death of the cellular elements in the culture, it was impossible to estimate the synergistic effect of EN. However, the proliferation suppression index was essentially lower if the dosage was decreased. Meanwhile, the combined influence of the weak electromagnetic field and the preparation appeared to be significantly higher than that observed upon individual influence of the DNA synthesis inhibitors in question. Under the combined influence of the preparations and EN, the suppression level of labelled thymidine inclusion was virtually the same as that observed under the influence of the chemical preparations taken in significantly higher amounts (1 and 0.5 TD).
4. The colonization capacity of the tumor cells under the influence of EN and chemical preparations.
The colonization activity of the tumor cells was estimated using dorosiliconized capillaries. The tumor cells in the amount of 500000 cells/ml in the complete medium of RPMI-1640 with 10% calf embryonic serum were mixed together with 0.32% agar prepared with distilled water and placed into a capillary. The capillaries were incubated for 14 days at 37 degrees C under the atmosphere containing 5% of carbon dioxide. An agglomerate of at least 50 cells was considered as a colony. The colonization efficiency (CE) was estimated as follows:
CE = (number of colonies/number of cells sown)*100%.
Three capillaries were filled for each point. The statistical analysis was carried out by the Student method.
The effects of EN and chemical preparations were studied with lymphoma EL-4 at the stage of logarithmic growth of tumor with the maximum thymidine inclusion therein.
The initial amount of colonies formed in a capillary equaled 20.3 ± 2.1, CE = 0.004%. In four hours, the number of colonies certainly reduced and achieved the value of 8.0 ± 0.6, CE = 0.0016%.
The same level was achieved in reduction of the number of colonies after four-hour incubation with vinchristine (for 1 TD, the number of colonies equaled 7.0 ± 0.6, CE = 0.0014%). Upon incubation with metatrexate, the inhibition effect was significantly lower (for 1 TD, the number of colonies equaled 16.0 ± 1.4, CE = 0.0032%; for 0.1 TD, the number of colonies equaled 16.0 ± 1.3, CE = 0.0032%). The combined effect of EN and chemical preparations did not result in further increase in the inhibiting activity with respect to the colonization process in the culture of lymphoma cells (for EN + vinchristine, the number of colonies equaled 8.0 ± 0.5, CE = 0.0016%; or EN + metatrexate, the number of colonies equaled 7.0 ± 0.6, CE = 0.0014%).
The number of colonies in the control capillaries was virtually invariable with respect to the incubation time.
On the basis of the experimental results obtained in these series, we can conclude that the weak electromagnetic field, generated by EN inhibits the colonization activity of the lymphoma tumor cells at the level provided by vinchristine taken in a higher concentration of 1 TD. At the same time, EN is a significantly more effective inhibitor of tumor colonization in the culture as compared to metatrexate. Due to its high inhibiting activity, it was impossible to demonstrate synergistic effect of EN with chemical preparations. Inhibiting of colonization of tumor cells in the culture is a good parameter to predict inhibition of tumor metastasizing in the organism.
5. The influence of EN on intracellular mitohondria dehydrogenases of tumor cells in the culture.
The working activity of cellular enzymes was estimated by the intensity of inclusion and reduction of tetrazolium salts (T.Mossman, 1983). This method is based on the study of the capacity of some mitohondria dehydrogenases of living and actively functioning cells to reduce tetrazolium salts, in particular MTT bromide. In this case, pale yellow water-soluble substrate (MT) is converted into dark blue crystals of formazane, which is insoluble in water.The reaction intensity is measured quantitatively by the colorimetric method. The amount of formazane formed serves as a criterion for activity of redox enzyme reactions in living cells under the influence of various agents. Upon incubation with EN, chemical preparations, or combination thereof, the tumor cells were dripped in triplet into 96-hole boards in the amount of 50000 cells per hole in the volume of 100 microliters. Into every cell, 25 microliters of MTT (Sigma) was added in the concentration of 5 mg/l of physiological solution. Then, after a three-hour incubation at 37 C under the atmosphere containing 5% of carbon dioxide, 150 microliters of isopropanol was added into every hole, and the board was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes. Finally, 100 microliters of supernatant liquid was taken from every hole and dripped into clean holes of a 96-hole board, and the color index was determined using a miltiscan (MCC 340 P, Lab System) at the wavelength of 540 nm.
Analysis of the parameters obtained by means of the MTT test revealed the following regularities. If the color index of tetrazolium inclusion in the tumor cells before the beginning of any actions equaled 0.132 ± 0.012; then upon a four-hour incubation with EN, this parameter significantly decreased to 0.150 ± 0.012. This comprised 52% of the control value. The same value of the color index was obtained upon incubation of the cells in the presence of vinchristine taken in the maximum concentration (0.153±0.006, 51% of the control value). The combined influence of EN and vinchristine did not result in further suppression of dehydrogenase activity (0.149 ± 0.009, 54% of the control value). Metatrexate was a significantly less effective inhibitor of the metabolic activity of the tumor cells, because the color index upon incubation with metatrexate decreased only to 0.257 ± 0.020 that equaled 82% of the control value for the metatrexate concentration of 0.1 TD. Upon the increase of the metatrexate concentration up to 1 TD, the degree of dehydrogenase suppression was invariable (0.243±0.012, 77.8% of the control value). At the same time, the combined influence of EN and metatrexate resulted in a certain and significant increase in inhibition of enzyme activity (0.135±0.005, 57% of the control value, p < 0.05).
In general, we can conclude that EN results in significant structural and functional disorders in the tumor cells. The mechanism of its inhibiting activity is similar to the mechanism of vinchristine effect. Moreover, the combined application of EN with chemical preparations significantly strengthens their tumoricidal properties; therefore, application of small doses of preparations together with EN results in the same effect as the action of preparations taken in the maximum doses.
Conclusions: In the first series of investigations, it was discovered that EN
administration improved the subjective estimate of functional status and quality of night sleep (33%
of cases), somewhat improved the phychoemotional status (17% of cases), and significantly activated
phychomotor reactions (67% of cases). As to neurodynamic functions, they did not virtually change
in comparison with the parameters of the initial investigation.
Administration of EN did not produce any significant effect on gas
exchange. At the same time, a favorable dynamics of some immunological and hematological parameters was
observed. In particular, this fact was indicated by the expressed tendency to increase in the overall number of
leukocytes (100% of cases), absolute number of lymphocytes (67% of cases), and monocytes (50% of cases).
We observed normalization of thrombocyte (50% of cases) and erythrocyte (33% of cases) germs of hemogenesis.
The results of immunological tests indicate the positive influence
of EN on activation of the elements of cellular immunity appearing in predominance of the most active
lymphocytes (T-lymphocytes) fraction in blood. Thus, for 67% of the examinees, the ratio of T-general
lymphocytes to T-active cells was below one, that indicated the effect of mobilization of the
receptor structures in the cell membrane of T-lymphocytes and could indicate a certain
immunopotentiation effect.
In general, the results obtained enable us to consider the
possibility to increase the immune potential of blood upon EN administration for preventive purposes.
The results of ultrasound investigation of gallbladder indicate
the favorable influence of EN on its motor and evacuator functions. This effect appeared as the
strengthened expression of contraction capacity of the gallbladder by 7 to 10% confirmed by its
decreased volume at the level of sugar and milk load. The initial volume of gallbladder was completely
retained by the sample control time that can indicate the activated billation function of smaller
(endohepatic) billary ducts. A more expressed effect was observed for the hyperkinetic type of reaction
to the load sample that indicates a possible efficiency of EN for diskinesia of billary ducts and chronic cholecystitis.
In the second series of investigations, the possibility of EN application
was estimated for maintenance of the optimum functional status and working capacity of the operator
upon simulation of a four-hour flight under comfortable conditions and under the influence of thermal
loading (1 hour at the temperature of +55 degrees C). The most significant result of EN application
included the improved quality of operator work (1.5-fold) and the increased efficiency factor
(by 6 to 10%) considering the factor of training (Figs. 11 and 12) in the second investigation
with a simulator. Under the conditions of thermal load, the subjective estimate of status in work
upon EN administration did not decrease, the physiological cost of work increased, and the quality
of operator work improved by 8% that, in general, indicates the possibility to use EN for maintenance
of operator working capacity under the extreme conditions of work.
Thus, the results of EN examinations indicate the favorable and
optimizing effect on the functional status and operator working capacity of practically healthy persons.
Conclusions: In the opinion of some researchers, for treatment of postoperative
intestinal paresis with predominant damage of its distal sections, it is expedient to use the per rectum
method of introduction; in the case of disordered function of proximal GIT sections, EN should be
introduced per os. In the case of generalized damage of all the GIT sections, both techniques can be
used simultaneously (9).
In our opinion, in most cases, we should prefer peroral application
of EN, because only in this case the effect concerns all the GIT sections and the related vegetative,
endocrine, lymphatic, and other systems. Thus, the maximum effect on the status of other systems and
the whole organism is achieved.
As to the rate of EN administration per os (one capsule is used once),
nowadays, we can arbitrarily distinguish the following most often techniques yielding the most effective
results in diseases: In some cases, it is indicated to apply EN otherwise. Then one
capsule can be used repeatedly: The most optimum techniques for EN application with the
maximum individualization are developed now with direct participation and under the supervision
of the ECOMED Research and Production Association.
1. Extension of the list of indications for application of the existing EN models.
2. Development of new EN models with the maximum specialization for various situations.
ECOMED Research and Production Association now realizes
research and development of new models of specialized EN. Meanwhile, the major trend concerns
development of new parameters of the electric signals generated by EN during application. In particular,
ECOMED studies the characteristics, which do not simulate the electric activity of GIT and produce
a more significant effect on other systems of the organism. The parameters chosen selectively
affect the activity of the immune, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems, the status of
various kinds of metabolism, as well as the neuroendocrine centers of the central nervous system.
The EN articles produced and developed by the ECOMED
Research and Production Association are classified into several types:
Efficiency of EN under physical and mental overloading
(Patent "Mehtod of Working Capacity Restoration" N 96111947 dated 26.06.96)
The investigation of the EN efficiency for prevention and correction
of functional (prenosological) disorders in relation to the GIT organs for practically healthy persons (the
first series of investigations) and for maintenance of working capacity under the conditions of simulated
stressogenic factors of flight work (the second series of investigations) were carried out on the basis of
the State Research Institute, Russian Federation Ministry of Defense (Institute of Aviation and
Space Medicine). The report dated March 25, 1995 was signed by Professor I.B.Ushakov, assistant
Director of the Institute; the program of investigations was approved by the ECOMED Research
and Production Association.
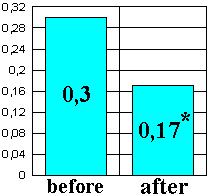
Figure 11. Time of erroneous actions per 1 minute (seconds) on the background of EN administration.
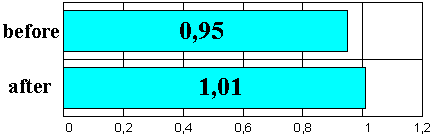
Figure 12. Factor of efficiency (arbitrary units) on the background of EN administration.
Methods of EN application
On the basis of the statistical material collected on EN application,
it becomes clear that the techniques of EN application are rather individual and depend upon the
patient's age, pathology, and status as well as some other factors.
Perspective development of autonomous git electrostimulation
Taking into consideration the experience of clinical application of EN,
the statistical materials collected, and the experimental data, ECOMED Research and Production
Association underlines the following priority guidelines of research works on development of autonomous
GIT electrostimulation:
|
Symmetric metal capsule generating the single-type signal (monoprogram processor) | |||||||||||||
|
Asymmetric metal (rubber, ceramic) capsule with multiprogram processor and built-in timer switching the regimes | |||||||||||||
|
Asymmetric metal (rubber, ceramic) capsule with multiprogram processor and switching the regimes | |||||||||||||
| Type 68 - 73 | Articles for special purposes including those with injection, orientation, radio channel, and diagnostic facilities |
2.1. Electronic Muscular Stimulator
(Electronic Normalizer, type 06)
Recommendations and explanations
Turns on automatically when put in body’s humid environment.
Stimulates and restores efficiency of muscles of vagina and uterus, of muscles of urinary
and gall-bladder, of peristalsis, of smooth muscles of large intestine and of rectum.
Normalizes lipide metabolism (general cholesterol, cholesterol of lipoproteins of low and
high density, triglycerides), improves immunity (IgA , IgE
, IgE
 ).
).
The procedure duration is no more than 20 minutes, up to 100 minutes a day.
Side effects:
3. Improvement of techniques for EN application.
In this respect, development of the optimum therapeutical schemes is of a special interest:
Therefore, recent concepts of some authors on the autonomous electrostimulator of GIT as a facility to activate GIT in intestinal pareses and malfunctions of billary ducts (9), actually indicate only few real changes, which take place on the background of EN application.
This broad spectrum of activity, high clinical efficiency in heavy diseases, absence of contraindications (excepting intestinal obstruction) make EN a therapeutical facility of future for treatment of quite different pathological processes. Unique effects observed in some diseases cannot be achieved using other facilities known in medicine.
It is especially important that the EN treatment is medicament-free and complex; therefore, it excludes side and allergic effects, which are characteristic virtually for all pharmacological preparations; and the similar result cannot be achieved by means of pharmacological therapy.
As is now discovered, EN can be applied not only as a medicine
but as a facility for prevention of development or exacerbation of pathological processes. This phenomenon
is associated with the fact that regular EN administration causes certain positive changes in a human
organism: neuroendocrine system comes to a higher level of functioning, and adaptation readiness
increases; hence, the resistance of the organism increases with respect to external overloading and
diseases; various kinds of metabolism change to normalization, in particular, lipid metabolism, that
prevents the development of atherosclerosis (and, hence, coronary heart disease and insult, which
are the major causes of death in the world); antitumor resistance increases that prevents the
development of malignant tumors, etc. In general, these changes in the human status are inevitably
accompanied by improvement of quality and length of life.
References
Note
The institutions of the Presidential Medical Center of Russian
Federation and former 4th Head Department of the USSR MInistry of Health Protection received
and receive now only the articles produced by the ECOMED Research and Production Association.