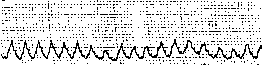
"APPROVED"
General Director of ECOMED Research and Production Association
S.A.Khvorostov
/signature/
Seal: ECOMED Research & Production Association Company Limited (Moscow)
State Registration No. 9624 |
"APPROVED"
Director of the State Coloproctology Research Center of the Russian Federation Ministry of Public Health
Corresponding Member of the Academy, Professor
G.I.Vorobiov
/signature/
Seal: State Research Center of Coloproctology,
Russian Federal Ministry of Public Health and Medical Industry |
R E P O R T
clinical applications of the Autonomous Electrostimulator of Gastrointestinal Tract and Mucous Membranes (AES GIT & MM) - Electronic Normalizer produced by the ECOMED Research and Production Association
Moscow, 1997
ELECTROSTIMULATION is one of the methods to affec the organism with electric current in order to excite or strengthen the functions of particular organs. Electrostimulation is based on the process of substitution of a defective nervous impulse, which generated in the organism, by an electric stimul; as a result it is possible to start the whole mechanism controlling the nervous and muscular system. With respect to technical characteristics of the stimulating current (frequency and shape of impulse, mode, etc.) as well as the method of application of electrostimulation, the lost functions are restored, primarily, contractibility of muscular structures that strengthens peristaltic activity in the gastrointestinal tract, increases the power potential of intestinal muscles and the whole organism, increases the activity of fermentative systems, imporves blood circulation of the stimulated organ and blood circulation in the whole.
For many years, the State Coloproctology Research Center has been designing and intriducing into clinical practice various methods for electrostimulation of the organs in the gastrointestinal tract as well as equipment providing the said electrostimulation. Under monitoring of the objective methods of functional status of the organs in the gastrointestinal tract, we designed the parameters of stimulating current, primarily, in the experiments with animals and then in clinics using various methods of cutaneous and intracavitary stimulation, as well as stimulation by means of inoculated electrodes. The results of this grand study were reported in the first and second conferences on the electrical stimulation of organs and tissues and published in periodic press in 1975 (Kaunas) and in 1979 (Kiev).
Since 1995, the State Coloproctology Research Center has been applying in their therapeutical practice the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer produced by the Ecomed Research and Production Association. With respect to its technical characteristics, the electronic normalizer complies with Technical Specifications No. 9444-014 - 11555014 - 95.
For this period, we have accumulated a great clinical experience in application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer for treatment of various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
In our Center, this stimulator is widely applied for treatment of patients suffering from chronic stasis of large intestine, syndrome of irritated large intestine, weakness of muscles of pelvic bottom, insufficience of anal sphincter of first and second degree, as well as for prevention of postoperative paresis of the gastrointestinal tract. But the most common application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer is connected with treatment of chronic constipations, which are typical in developed countries for each second or third adult, while females have this disease much more frequently than males.
Normal evacuation of intestines is recognized as two times every day to once every two days, while the defecation act should not be accompanied with significant efforts, and this act should be followed by the feeling of complete evacuation of intestines.
Evacuation of intestines less frequently than two times every week is recognized as constipation.
Chronic constipations are classified into cologenic (where the strongest changes in the functional status are discovered in the proximal sections of large intestine) and procrogenic (with disordered motor and evacuation functions of large intestine and the closing mechanism thereof).
The differential diagnostics is performed by means of examination of the functional status of large intestine and rectum (which are described below), as well as clinical, rentgenological, endoscopic, and other methods.
METHODS FOR ESTIMATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
- ENTEROCOLOGRAPHY is the method for estimation of the functional status of large and small intestines by recording their bioelectrical activity. Recording was performed using the ENTEROGRAPH and COLOGRAPH instruments and cutaneous electrodes installed in the projection of the intestinal section under investigation.
- ELECTROMANOMETRY is the method for estimation of the motor activity of large intestine by recording intracavitary pressure using a five-channel probe introduced into the opening of large intestine. We studied the background and stimulated (digestive and mechanical) motor activity. We estimated the index of motor activity, tone of intestinal wall and intracavitary pressure, as well as amplitude and temporary characteristics and wave spectrum of motor activity.
- SENSOMETRY is the method for determination of sensitivity of rectum with respect to filling. This is realized using dozed step-wise irritation of rectum with a baloon introduced in its opening and registration of subjective feelings of the patient.
Control of passage and work of the autonomous electrostimulator was performed using a Medicor ELECTROMIOGRAPH by means of determination of the amplitude of characteristic electric signal detected by the cutaneous electrodes, which were installed in the projection of various organs in the gastrointestinal tract The location of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes was determined by recording the maximum amplitude of the signal accompanied by sound indication.
DESCRIPTION OF PATIENTS
The autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer was applied to treatment of 66 patients in the age of 17 to 73 (the average age was 54.5), including 47 females and 19 males.
Table 1. SEX AND AGE DISTRIBUTION OF PATIENTS
| SEX | < 20 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | > 70 | TOTAL |
| Males | - | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 19 |
| Females | 3 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 47 |
| Total | 3 | 11 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 84 | 1 | 66 |
Thus, the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes was applied essentially to the patients of the middle age group, which with the females / males ratio of 2.3.
Analysis of the kind of professional activity (professions) of the patients suffering from constipations in the described group showed prevailing of persons occupied with intellectual labour - 42 (63.7 %), including economists, teachers, programmers, medical workers, and students. The remaining 15 patients (22.7 %) were retired, while 9 patients (13,6 %) were occupied in various kinds of active labour (drivers, workers, mechanicians, and agricultural workers).
Table 2. DISTRIBUTION OF PATIENTS WITH RESPECT TO DURATION OF DISEASE
Duration
of disease | Number of patients |
| Males | Females | Total |
| 1 to 2 years | 2 | 13 | 15 (22.7%) |
| 2 to 4 years | 10 | 23 | 33 (50.0%) |
| 5 years and over | 7 | 11 | 18 (27.3%) |
| Total: | 19 | 47 | 66(100.0%) |
The major complaint of these patients was disorder in regular evacuation of intestines that made some of them apply laxatives and purgative enemas. Independent irregular stool was observed for 27 patients (40.9 %).
Table 3. FREQUENCY OF INDEPENDENT STOOL OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC
CONSTIPATIONS
| Stool frequency | Males | Females | Total |
| once every 3 days | 9 | 6 | 15 (55.5%) |
| once every 4 - 5 days | 4 | 3 | 7 (25.9%) |
| once every week | 3 | 2 | 5 (18.6%) |
| Total: | 16 | 11 | 27(100.0%) |
As we can see from these data, males more frequently achieve incdependent stool due to strong and repeated muscle contractions and thus less frequently apply laxatives and purgative enemas; in this connection, such disease as hemorrhoid is depeloped more often by several times as compared to females.
The remaining 39 patients in the group under investigation regularly applied purgative enemas and laxative preparations (with gradual increase in the amount of applied laxative preparations). This categories of patients achieved stool by means of laxatives and urgative enemas once every two or three days.
As a result of comprehensive clinical functional examination of all the patients, who suffered from chronic constipations, they were classified into three groups with respect to the kind of disorders discovered: cologenic, proctogenic, and combined disorders.
Table 4. DISTRIBUTION OF PATIENTS WITH RESPECT TO KIND OF CHRONIC CONSTIPATION
| KIND OF CONSTIPATION | Males | Females | Total |
| COLOGENIC | 16 | 21 | 37 (56.0%) |
| PROCTOGENIC | 2 | 14 | 16 (24.3%) |
| COMBINED | 1 | 12 | 13 (19.7%) |
| Total | 19 | 47 | 66(100.0%) |
RESULTS OF BACKGROUND INVESTIGATIONS
Before starting treatment by means of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes, all the patients passed comprehensive functional examination.
Table 5. FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF LARGE INTESTINE (background investigation)
| DIAGNOSIS | ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY
(electrocolography)
index of
electrical activity | MOTOR FUNCTION
(electromanometry) |
index of
activity | percentage of
peristaltic waves |
Cologenic
constipations | 0.112 ± 0.011 | 1.022 ± 0.007 | 5.30 ± 0.92 |
Proctogenic
constipations | 0.151 ± 0.009 | 1.081 ± 0.005 | 8.42 ± 1.05 |
Combined
constipations | 0.127 ± 0.008 | 1.043 ± 0,002 | 7.26 ± 1.10 |
| NORMAL | 0.185 ± 0.004 | 1.140 ± 0.003 | 38.40 ± 2.10 |
Thus, all the patients showed a statistically reliable decrease in all the parameters of the electrical and motor activity of large intestine (p < 0.05) with respect to the mormal parameters.
In addition, the patients with proctogenic constipations and combined disorders showed a disorder in the sensitivity of rectum with respect to filling (three cases), muscle spasm of pelvic bottom (up to five cases), increased tone of internal sphincter with phenomena of disorder of its nervous reflector activity (ten cases).
APPLICATION TECHNIQUE OF THE AUTONOMOUS ELECTROSTIMULATOR OF
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT AND MUCOUS MEMBRANES - ELECTRONIC
NORMALIZER
Peroral application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes was carried out by all the 66 patients in the morning on an empty stomach in the presence of a physician. The stimulator was placed on the root of tongue and easily swallowed upon two or three gulps of water.
No difficulties were observed by the patients in swallowing; most patients noted some "pinching" on the surface of tongue at the moment of swallowing when the stimulator switched on upon contact with the electrolyte environment of the oral cavity due to the individual sensitivity of patients with respect to electric current.
The procedure for application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes was different in dependence of the discovered original functional background of the status of motor and evacuator activities of large intestine and rectum.
In the case of cologenic constipations, we applied two autonomous electrostimulators per a therapeutical course with the interval of two weeks. These patients used only the peroral method of introduction.
In the case of proctogenic disorders, we also used two electrostimulators per a therapeutical course: the first stimulator was applied per rectum for ten days in order to correct the disorders in the distal section of rectum (patients introduced the stimulator every day as a suppository for two to three hours; then it was removed upon exertion, treated, and stored in a dry place); on the eleventh day, the second stimulator was applied per os.
In the case of combined constipations, we also used first the rectal method of introduction and then two normalizers were applied per os with the interval of three to four weeks.
Before and after application of the electronic normalizer, the patients were subjected to general and special investigations and were examined by a physician. The effect of electrostimulation was estimated upon removal of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes from the organism.
RESULTS OF CLINICAL FUNCTIONAL INVESTIGATIONS DURING AND AFTER APPLICATION OF THE AUTONOMOUS ELECTROSTIMULATOR OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT AND MUCOUS MEMBRANES - ELECTRONIC NORMALIZER
When the normalizer was introduced in the organism, monitoring of its location and functioning was performed for 66 patients. In five to ten minutes upon swallowing, switching of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes was detected by means of a myograph. The stimulator functioned for all the 66 patients that was indicated by the characteristic oscillogram on the display of the electromyograph, while appearance of a series of impulses was accompanied by a sound signal, which was distictly heard by the patients that provided an additional positive psychotherapeutical effect.
The maximum amplitude of the electric signal for 45 to 60 minutes upon application was registered in the projection of stomach, then we observed a shift of the signal along the small intestine, where the capsule stayed for 3 to 12 hours in average, then it moved to the zone of blind intestine. The duration of stay of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes in the large intestine was significantly ranged for different patients in dependence of the degree of pathological changes in the large intestine. We noted a change in the speed of motion of the capsule in the different sections of gastrointestinal tract. For the patients with constipations, the maximum stay of the capsule was observed in the left sections (sigmoid intestine and rectum). A long stay of the capsule in various sections of the large intestine was essential for diagnostics and indicated the most changed section of this intestine. Therefore, a longer time was necessary for the capsule for excitation of peristaltic activity.
Independent removal of the electronic normalizer with stool was observed forall the 66 patients in 2 to 7 days upon application. The information of stay of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes in the organism is represented in Table 6.
Table 6. STAY OF THE AUTONOMOUS ELECTROSTIMULATOR OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT AND MUCOUS MEMBRANES IN THE PATIENTS WITH DISEASES OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
DURATION OF STAY
(hours) | NUMBER OF PATIENTS |
| Absolute number | Percentage |
| < 24 hours | - | - |
| 24 to 48 hours | 4 | 6.1 |
| 48 to 72 hours | 20 | 30.3 |
| 72 to 96 hours | 28 | 42.4 |
| 96 to 120 hours | 8 | 12.2 |
| > 120 hours | 6 | 9.0 |
| Total | 66 | 100.0 |
Upon the second application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes within the same therapeutical course, 18 patients showed a decrease in the stay of the capsule in the organism by 12 to 24 hours in average with respect to the first application that indicates activation of the peristaltic function of intestines already upon the first application.
Subjective feelings of the stimulator in the organism were reported by 58 patients (87.9 %): they noted the phenomena of local muscular contraction in the front abdominal wall, twitching in the muscles of hip, which were painless and did not cause any unpleasant feelings. Only in one case a female patient with asthenic constitution had so strong leg muscular contractions that prevented her normal walking. These patients noted periodically the feeling of "movements" in their intestines. In other cases, the patients showed no feelings.
ESTIMATE OF EFFICIENCY OF APPLICATION OF THE AUTONOMOUS ELECTROSTIMULATOR OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT AND MUCOUS MEMBRANES
The efficiency of treatment by means of the electronic normalizer was estimated using the subjective information (frequency of stool and complete evacuation of intestines) and the information of clinical functional dynamic investigations of gastrointestinal tract. We considered the results as good in the case of stable normalizing of the stool frequency (once ot twice every two days) and disappearance of the symptoms of discomfort during and after defecation. We considered the results as satisfactory in the case of independent stool, which, however, was irregular; moreover, for the patients with proctogenic constipations, we observed a decrease in the symptoms of discomfort during defecation. The absence of any improvement was considered as unsatisfactory results.
Table 7. RESULTS OF TREATMENT BY MEANS OF THE AUTONOMOUS ELECTROSTIMULATOR OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT AND MUCOUS MEMBRANES
KIND OF
CONSTIPATIONS | RESULTS OF TREATMENT |
| GOOD | SATISFACTORY | UNSATISFACTORY | TOTAL |
| COLOGENIC | 32 | 4 | 1 | 37 |
| PROCTOGENIC | 12 | 2 | 2 | 16 |
| COMBINED | 10 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| TOTAL | 54 (81.8%) | 8 (12.1%) | 4 (6.1%) | 66 (100.0%) |
Thus, in the whole, among the patients, who suffered from chronic constipations, upon treatment by means of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer, we observed good results for 81.8 % patients, satisfactory results for 12.1 % of patients, while no effect was observed for only four patients that made 6.1 %.
Our analysis of the results of treatment with respect to the kind of discovered functional disorders showed that the patients with cologenic constipations (37 patients in total) had the positive result of treatment in 32 cases that was indicated by appearance of independent regular stool (with the frequency of once every one or two days) and normalized functional parameters of the activity of large intestine. Four patients showed incomplete normalizing of stool that required application of additional methods of treatment. In one case, a female patient, who suffered from constipations for fifteen years and regularly applied the preparations of senna to evacuate her intestines, even double application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes did not produce any positive effect.
We carried out a comparative analysis of the results of therapy of cologenic constipations with respect to the presence of independent stool before starting treatment. For 17 patients with cologenic constipations, who had before treatment irregular but independent stool (without application of any laxatives or purgative enemas), we observed positive effects in all the cases; therefore, this category of patients shows the most favourable results after application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes (it is interesting to note that most patients in this group were males: 13 patients of 17).
For 16 patients with proctogenic constipations, our scheme of treatment resulted in normalized stool in 12 cases; in addition, these patients showed facilitated process of defecation and decreased symptoms of discomfort after treatment. In two cases after the applied scheme treatment using the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes, we observed appearance of independent stool; however, these patients still had difficulties in evacuation of rectum.
In the group of patients with combined disorders (13 patients), good results were observed only for ten patients, satisfactory results were observed for two patients, while we failed to achieve any positive effect in one case.
For all the 66 patients, we studied the functional status of large intestine by means of electrocolography and mamometry immediately after removal of the first and second capsules and in four weeks after completion of treatment. We observed positive dynamics in the parameters of electrical and motor activities of large intestine for 62 patients (93.9 %). The results of functional investigations of the electrical and motor activities of large intestine performed upon completion of the therapeutical course using the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer are represented in Table 8.
Table 8. FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF LARGE INTESTINE (after treatment)
| DIAGNOSIS | ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY
(electrocolography)
index of
electrical activity | MOTOR FUNCTION
(electromanometry) |
index of
activity | percentage of
peristaltic waves |
Cologenic
constipations | 0.162 ± 0.012 | 1.138 ± 0,007 | 28,31 ± 1.92 |
Proctogenic
constipations | 0,181 ± 0.011 | 1.131 ± 0,008 | 35,12 ± 1.75 |
Combined
constipations | 0.167 ± 0.010 | 1.135 ± 0.009 | 29.35 ± 2.10 |
| NORMAL | 0.185 ± 0.004 | 1.140 ± 0.003 | 38.40 ± 2.10 |
After the therapeutical course by means of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer, the parameters of electrical and motor actovities were significantly increased (statistically reliable with respect to the background investigatin, p < 0.05) and practically achieved the normal lower limit.
As illustration, we represent below the diagrams of changes in the motor activity index (Figure 1) and the wave spectrum (Figure 2) of the large intestine in the whole for all the group of patients under investigation. These diagrams indicate the dynamics of changes in the structure of motor activity: we observe an increase in the motor activity inder (in average, by 24.6 %) and an expressed increase in the fraction of peristaltic waves, as well as appearance of propulsive contractions.
Figure 1. MOTOR ACTIVITY INDEX OF LARGE INTESTINE BEFORE AND AFTER APPLICATION OF THE AES GIT & MM

Figure 2. WAVE SPECTRUM OF MOTOR ACTIVITY BEFORE AND AFTER APPLICATION OF THE THE AES GIT & MM

It is interesting to note that before and after removal of the capsule we observed gradual normalizing of the parameters of motor function of large intestine. The characteristic changes were observed in the ratio of motor activity waves: fraction of the medium- and high-amplitude peristaltic contractions increased. As a result of application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes, for 41 patients (62.3 %), we observed normalizing in the tone of intestinal wall and the value of pressure in the opening.
As a clinical example, we give below the medical history of femal patient T., aged 54, who had been suffering from chronic constipations for more than ten years. This patient showed complaints for the absence of independent stool, applied laxatives for a long time, and at last only purgative enemas could help her. In thr course of functional investitaion before application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes, wre discovered a strong depression in the motor activity of large intestine (index of activity was 1.03) on the background of decreased tone of the intestinal wall: akinetically atonic type of motor activity. We observed a shift in the wave spectrum of motor activity towards the low-aplitude segmentary contractions (Figure 1a). Upon application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes, this patient had independent stool on the third day without evacuation of the capsule, which was removed only during the next defecation on the fourth day. Afterwards, this patient retained independent stool with the frequency of every one or two days. In the course of functional investigation, we noted a significant increase in the motor activity (index of activity increased by 45% and achieved the value of 1.54); we also observed recovery of the tone of intestinal wall and appearance of peristaltic complexes (Figure 1b). This patient was recommended to apply the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes for the second time in three months in order to strengthen the effect.
| Figure 1a |
|
Figure 1b |
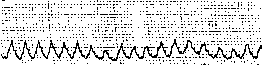 |
|
 |
C O N C L U S I O N
Electrostimulation of gastrointestinal tract by means of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer is a pathogenetically substantiated and effective method for treatment of diseases of the digestive system. This kind of electrostimulation actively affects the nervous and muscular systems of digestive tract, recovers the motor and evacuator functions, and also promotes improvement of feeling, increases working capacity, and normalizes the phychoemotional status of patients.
It is necessary to note that, in accordance with the results of investigations performed in the State Coloproctology Research Center of the Russian Federation Ministry of Public Health, the as compared to similar constructions of other producers, autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer produced by the Ecomed Research and Production Association shows a higher efficiency and absence of any side effects.
The electronic normalizer is a powerful instrument in therapy of various forms of chronic constipations and other diseases of gastrointestinal tract, which are widespread in the world in recent years.
Upon application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer by the patients, who suffer from diseases of gastrointestinal tract, a strong positive effect was achieved in total in 93.9% of cases, while complete normalizing of stool was observed for 81.8% of patients. Using the ability to apply the electrostimulator gradually to all the sections of gastrointestinal tract, we can discover the sections with decreased motor activity that is of a significant diagnostical importance, in addition to the therapeutical effect.
No side or adverse effects were observed upon application of the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer.
In accordance with the facts aforementioned, the autonomous electrostimulator of gastrointestinal tract and mucous membranes - electronic normalizer can be recommended for application in the medical practice not only in under stationary but also ambulatory conditions and at home after prior consultation with a physician.
Manager of the Laboratory
for Clinical Pathophysiology
and Physical Methods of Therapy,
candicate of medical sciences |
|
/signature/ |
|
A. P. Tupikova |
Senior researcher,
candidate of medical sciences |
|
/signature/ |
|
L. F. Podmarenkova |
Senior researcher,
candidate of medical sciences |
|
/signature/ |
|
M. V. Eliseeva |

Original products have laser marking on the box with written title "Electronic normalizer", factory number, little star and the RPA "Ecomed" trade mark.